The US State Department on Tuesday imposed visa bans on a former European Union commissioner and four others, accusing them of forcing American social media platforms to censor users and their viewpoints.
US Secretary of State Marco Rubio said the five people targeted with visa bans “have led organised efforts to coerce American platforms to censor, demonetise, and suppress American viewpoints they oppose”.
“These radical activists and weaponised NGOs have advanced censorship crackdowns by foreign states – in each case targeting American speakers and American companies,” Rubio said in a statement.
Rubio did not initially name those targeted, but US Under Secretary for Public Diplomacy Sarah Rogers identified them on X, accusing the individuals of “fomenting censorship of American speech”.
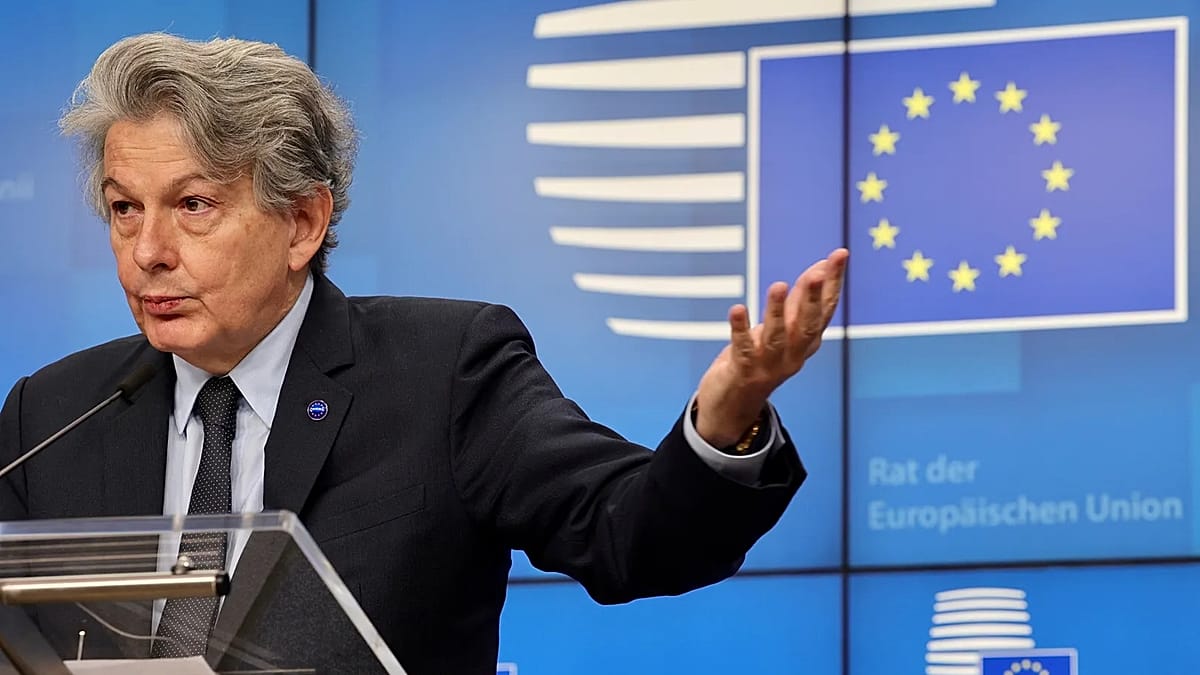
The most high-profile target was Thierry Breton, a French former business executive who served as European Commissioner for the Internal Market from 2019 to 2024.
Rogers described Breton as the “mastermind” of the EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA), the EU digital sphere rulebook that imposes content moderation and other standards on major social media platforms operating in Europe.
The visa bans also targeted Anna-Lena von Hodenberg and Josephine Ballon of the German nonprofit HateAid, Clare Melford, co-founder of the UK-based Global Disinformation Index, and Imran Ahmed, the British chief executive of the US-based Center for Countering Digital Hate.
Breton responded to the visa ban on X by writing: “Is McCarthy’s witch hunt back?”
“As a reminder: 90% of the European Parliament — our democratically elected body — and all 27 member states unanimously voted for the DSA,” Breton added. “To our American friends: ‘Censorship isn’t where you think it is.'”
French Foreign Minister Jean-Noël Barrot said France “strongly condemns” the visa restrictions, adding that Europe “cannot let the rules governing their digital space be imposed by others upon them”.
“The Digital Services Act (DSA) was democratically adopted in Europe … it has absolutely no extraterritorial reach and in no way affects the United States,” Barrot said.
The three nonprofits have also rejected Washington’s claims and criticised Tuesday’s visa ban decision.
The letter that started it all?
Rogers specifically referenced a letter Breton sent to X owner Elon Musk in August 2024, ahead of an interview Musk planned to conduct with then-US presidential candidate Donald Trump.
In the letter, Breton warned Musk that he must comply with the Digital Services Act, according to reports at the time.
Rogers accused Breton of having “ominously reminded Musk of X’s legal obligations and ongoing ‘formal proceedings’ for alleged noncompliance with ‘illegal content’ and ‘disinformation’ requirements under the DSA.”
In February, US Vice President JD Vance used one of his first major speeches after taking office to criticise what he described as censorship efforts in Europe, delivered at the Munich Security Conference.
He claimed that leaders had “threatened and bullied social media companies to censor so-called misinformation,” citing the example of the COVID-19 lab leak theory.
The DSA stipulates that major platforms must explain content-moderation decisions, provide transparency for users and ensure researchers can carry out essential work, such as understanding how much children are exposed to dangerous content.
The EU digital rulebook has become a rallying point for US conservatives who see it as a weapon of censorship against right-wing voices thought in Europe and beyond, an accusation Brussels denies.
The European Commission dismissed US censorship allegations back in August, calling them “nonsense” and “completely unfounded”.
Earlier this month, the European Commission found Musk’s X in breach of DSA rules on transparency in advertising and verification methods, sparking another uproar in the US.
Romane Armangau contributed additional reporting.
Read the full article here